What is Cron?
Cron runs tasks automatically at specific time intervals. Using Cron, you can tell the server to run a backup script once every day at 00:00.
A Cron Job is the actual task you want to run on a schedule.
You can define the tasks and the schedule from your cPanel.
What is WP-Cron and what is the problem with it?
WordPress relies on WP-Cron to manage scheduled tasks, but it has some significant drawbacks. Unlike system cron, which executes tasks precisely as scheduled, WP-Cron is triggered on every page load. This can lead to performance issues on high-traffic sites.
Consider a backup plugin set to run weekly on a site with 1,000 daily page views. WP-Cron will fire 1,000 times, checking if it's time to run the backup. That's 7,000 unnecessary checks for a single task. With 1,000 page views per hour, this problem amplifies exponentially.
The Solution
To avoid performance issues, consider disabling WP-Cron and setting up a system cron job. This ensures tasks run precisely as scheduled, without relying on page loads.
1. Disable WP-Cron
You can disable WP-Cron is by adding the following code into your wp-config.php file
define('DISABLE_WP_CRON', true);
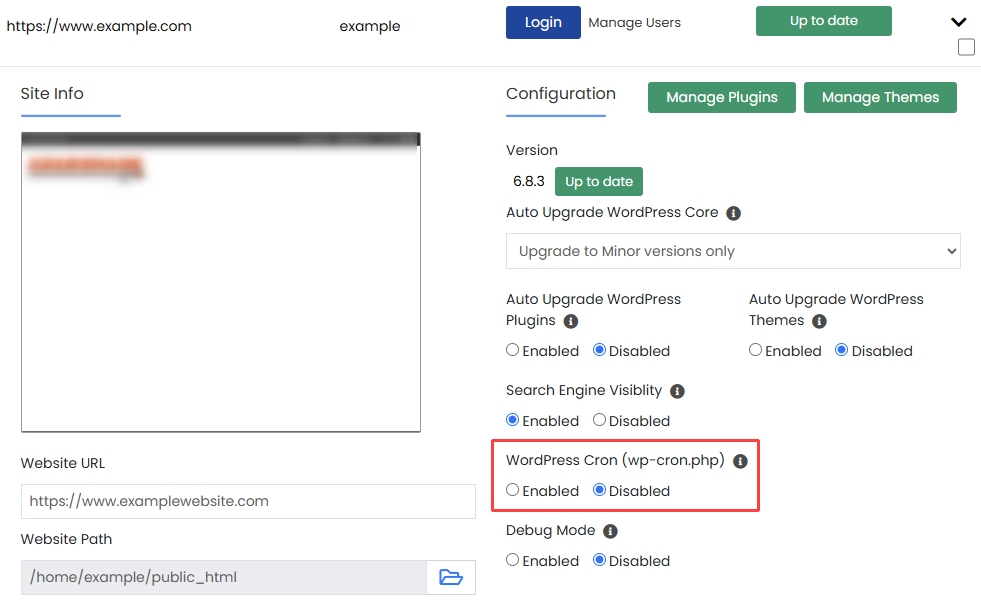
or, you can use WordPress Manager in cPanel, select the WordPress installation and set 'WordPress Cron (wp-cron.php) ' to disabled:
2. Create a Cron Job in cPanel
- Log in to cPanel. In the Advanced section, click on Cron Jobs.
- Under the Add New Cron Job section, you can choose from a number of different pre-defined schedules (common settings), You can choose 'Once per day' or 'Twice per day'.
-In the command field, Enter the WP-CRON URL like this example
wget -q -O - https://example.com/wp-cron.php?doing_wp_cron >/dev/null 2>&1
Replace example.com with your domain (and change WordPress installation folder if required).
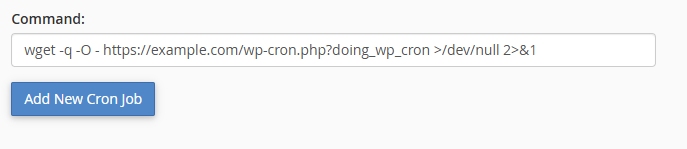
Click 'Add New Cron Job' and you are done.